Is Chromatin Found In Plant Or Animal Cells
Eukaryotic cells are found in plants, animals, fungi, and protists. They generally accept a nucleus—an organelle surrounded past a membrane called the nuclear envelope—where DNA is stored. There are a few exceptions to this generalization, such equally human red claret cells, which don't accept a nucleus when mature. Eukaryotic cells are typically larger than prokaryotic cells, ranging from effectually 10 to 100 μm in diameter. While many eukaryotes consist of multiple cells, in that location are also single-celled eukaryotes. Like leaner, animal cells take a plasma membrane, cytoplasm, and Deoxyribonucleic acid. However, you'll notice that the inside and outside of creature cells looks quite unlike from that of bacteria. For ane, animal cells don't have a cell wall. Instead, they have a cytoskeleton, a network of filaments composed of proteins. The cytoskeleton provides support and internal ship for the cell. In improver, most brute cells have a nucleus, a special organelle that stores DNA. The Deoxyribonucleic acid inside the nucleus is ordinarily organized into strings called chromosomes. The cytoplasm of animal cells is filled with a variety of organelles that assist the cells survive and reproduce. Hither are some cardinal cytoplasm-dwelling organelles and their functions: Organelle Function Centrosome The centrioles and pericentriolar material inside play a role in cell sectionalization and building microtubules Golgi appliance Modifies, sorts and packs proteins into transfer vesicles, and then they can go elsewhere in the cell or exist secreted Lysosomes & peroxisomes Help remove waste matter, break downward toxic compounds, and recycle prison cell structures Mitochondria Generate energy Ribosomes Synthesize proteins Rough endoplasmic reticulum Continuous with outer layer of nuclear envelope and has ribosomes embedded on the outer membrane; helps transport materials within the cell; segregates newly-made proteins for send by vesicles Smooth endoplasmic reticulum Split from the nuclear membrane, just continuous with the rough endoplasmic reticulum, and does not contain ribosomes; site of lipid synthesis, sugar metabolism and detoxification; helps send materials within the prison cell Vesicles Small bleary sacs that send materials within the cell; can fuse with the cell membrane to release contents Like animal cells and other eukaryotic cells, establish cells take a nucleus that stores their Deoxyribonucleic acid. However, institute cells differ from animal cells in several important ways. First, different animal cells, plant cells accept a cell wall, which is very different from prokaryotic jail cell walls. Institute cell walls have channels called plasmodesmata (sg. plasmodesma) that permit cells to communicate by passing sugars, ions, and fifty-fifty proteins and RNA from one prison cell to another. Fauna and establish cells both have mitochondria. Mitochondria utilize glucose and oxygen to acquit out cellular respiration and create ATP, a molecule that powers processes throughout the prison cell. In addition to mitochondria, plant cells also have special structures called chloroplasts that are essential to the process of photosynthesis. In this process, plants employ lite, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose, which can later be broken down past cellular respiration. Did you know that mitochondria and chloroplasts have their own DNA, separate and distinct from the DNA in the nucleus? Another structure that is present in establish cells, but non in creature cells, is the central vacuole. In plant cells, fundamental vacuoles are used to maintain turgor force per unit area by keeping the large vacuole filled with water to support the cell. Here are the structures that are unique to animal cells, assorted with the ones that are unique to establish cells: In Animal Cells Only In Plant Cells Only What is a eukaryote? A look at animal and found cells
1. Found and animal cells are eukaryotic, pregnant that they accept nuclei
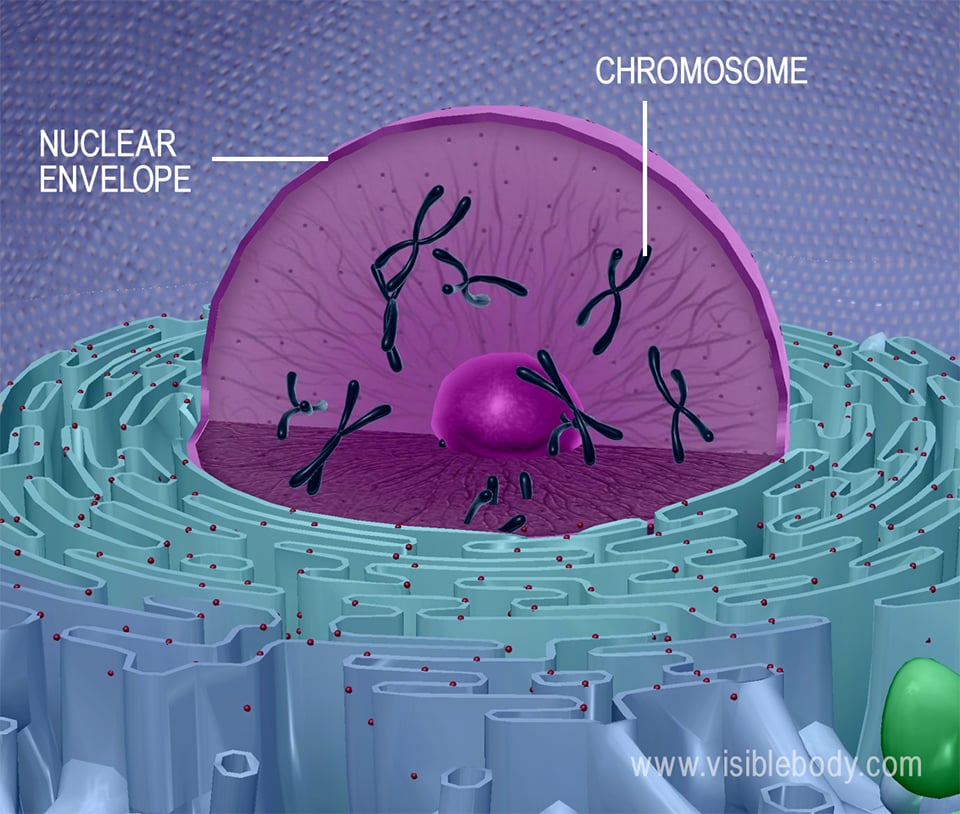
2. Animal cells are supported by a cytoskeleton, employ mitochondria to generate energy, and use lysosomes to assistance remove waste matter
Beast cell

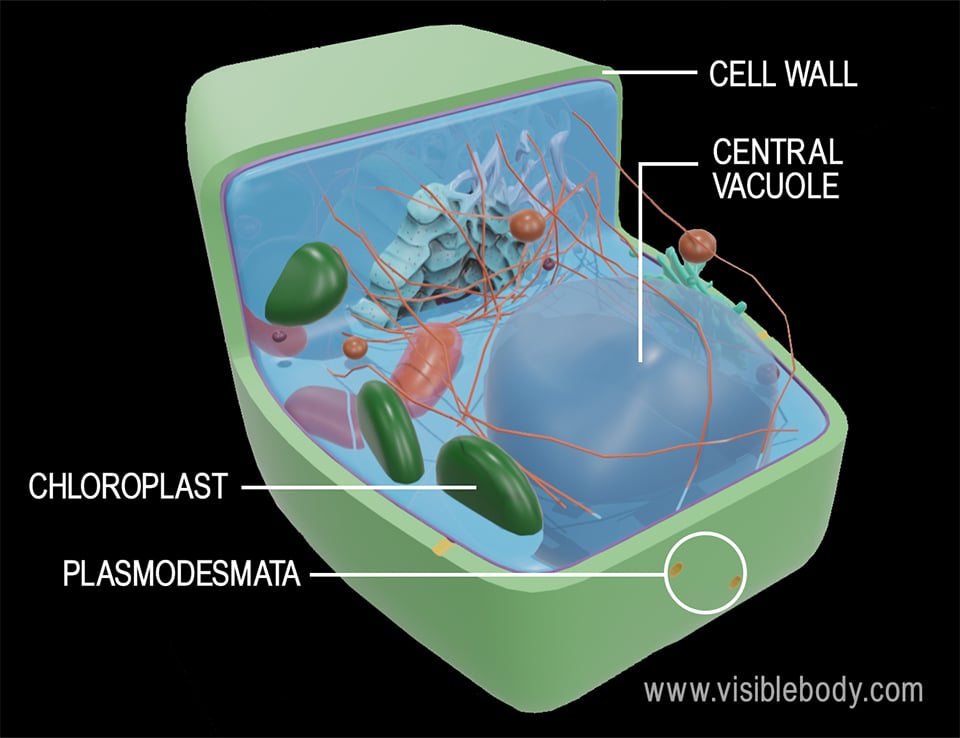
3. Institute cells are supported by a jail cell wall, use chloroplasts to carry out photosynthesis, and contain a big central vacuole that stores water
Plant cell

four. A quick comparing of plant and animal cells
Centrosomes
CentriolesPrison cell wall
Primal vacuole
Chloroplasts
PlasmodesmaVisible Torso Biological science
Learn more than


Source: https://www.visiblebody.com/learn/biology/cells/eukaryotic-cells
Posted by: jasperbution.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Is Chromatin Found In Plant Or Animal Cells"
Post a Comment